What is Alzheimer’s disease? 什么是阿尔茨海默病?
Alzheimer’s disease (阿尔茨海默病)is a brain disorder that slowly destroys memory and thinking skills and, eventually, the ability to carry out the simplest tasks. In most people with the disease — those with the late-onset type symptoms first appear in their mid-60s. Early-onset Alzheimer’s occurs between a person’s 30s and mid-60s and is very rare. Alzheimer’s disease is the most common cause of dementia (老年痴呆症)among older adults.
阿尔茨海默病是一种脑部疾病,它会慢慢破坏记忆力和思维能力,并最终破坏做简单事情的能力。在大多数患有这种疾病的人中,那些晚发型症状首次出现在60多岁。早发性阿尔茨海默氏症发生在人的30多岁到60多岁之间,这非常罕见。阿尔茨海默病是老年人痴呆症的最常见原因。
The disease is named after Dr. Alois Alzheimer. In 1906, Dr. Alzheimer noticed changes in the brain tissue of a woman who had died of an unusual mental illness. Her symptoms included memory loss, language problems, and unpredictable behavior. After she died, he examined her brain and found many abnormal clumps (now called amyloid plaques 淀粉样斑块) and tangled bundles of fibers 纤维束缠结 (神经原纤维 now called neurofibrillary, or tau, tangles).
这种疾病是以阿尔茨海默医生的名字命名的。1906年,阿尔茨海默博士注意到一位死于罕见精神疾病的女性脑组织发生了变化。她的症状包括失忆、语言问题和不可预测的行为。她去世后,他检查了她的大脑,发现了许多异常的团块(现在被称为淀粉样斑块)和纤维束缠结(现在被称为神经原纤维,或tau, 纤维缠结)。
These plaques (斑块)and tangles (缠结) in the brain are still considered some of the main features of Alzheimer’s disease. Another feature is the loss of connections between nerve cells (neurons) in the brain. Neurons (神经元)transmit messages between different parts of the brain, and from the brain to muscles and organs in the body. Many other complex brain changes are thought to play a role in Alzheimer’s, too.
大脑中的这些斑块和缠结仍然被认为是阿尔茨海默病的一些主要特征。另一个特征是大脑中神经细胞(神经元)之间的连接丧失。神经元在大脑的不同部分之间传递信息,并从大脑传递到身体的肌肉和器官。许多其他复杂的大脑变化也被认为在阿尔茨海默氏症中起作用。
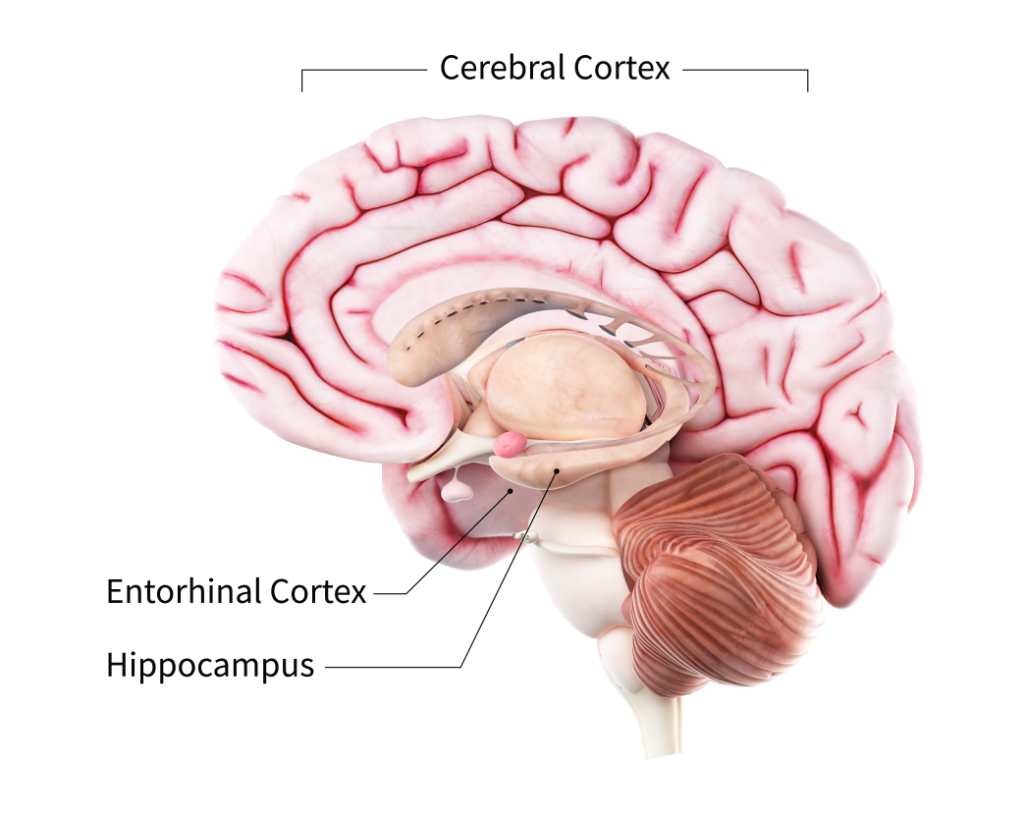
This damage initially takes place in parts of the brain involved in memory, including the entorhinal cortex (内嗅皮层,新脑或新大脑皮层)and hippocampus (海马体,或旧脑). It later affects areas in the cerebral cortex (大脑皮层[səˈriːbrəl ˈkɔːrteks]), such as those responsible for language, reasoning, and social behavior. Eventually, many other areas of the brain are damaged. (from nia.nih.gov)
这种损伤最初发生在大脑中与记忆有关的部分,包括内嗅皮层和海马体。它随后会影响大脑皮层的区域,比如负责语言、推理和社会行为的区域。最终,大脑的许多其他区域都会受损。
How to treat Alzheimer’s disease 如何治疗阿尔茨海默病
There’s no cure for Alzheimer’s, but there are treatments that may change disease progression, and drug and non-drug options that may help treat symptoms. Understanding available options can help individuals living with the disease and their caregivers (照顾者) to cope with symptoms and improve quality of life. (from alz.org)
目前阿尔茨海默氏症无法治愈,但有可能改变疾病进展的治疗方法,药物和非药物选择可能有助于治疗症状。了解可用的选择可以帮助患有这种疾病的个人及其照顾者应对症状并改善生活质量。
Alzheimer’s medicines can help with memory symptoms and other cognitive changes (认知变化). Two types of drugs are currently used to treat symptoms:
阿尔茨海默氏症的药物可以帮助治疗记忆症状和其他认知变化。目前用于治疗症状的药物有两种:
Cholinesterase inhibitors (胆碱酯酶抑制剂[ˌkoʊlə’nestəˌreɪs]). These medicines work by boosting levels of cell-to-cell communication. The medicines preserve a chemical messenger (化学信使)that is depleted in the brain by Alzheimer’s disease. These are usually the first medicines tried, and most people see modest improvements in symptoms.
胆碱酯酶抑制剂:这些药物通过提高细胞间的交流水平来起作用。这些药物保留了一种因阿尔茨海默病而在大脑中耗尽的化学信使。这些通常是用于第一次尝试的药物,大多数人症状略有改善。
Cholinesterase inhibitors (胆碱酯酶抑制剂) may improve symptoms related to behavior, such as agitation or depression. The medicines are taken orally or delivered through a patch on the skin. Commonly prescribed cholinesterase inhibitors include donepezil (Aricept, Adlarity), galantamine (Razadyne) and rivastigmine transdermal patch (Exelon).
胆碱酯酶抑制剂可改善与行为有关的症状,如躁动或抑郁。这种药物可以口服或通过贴在皮肤上的贴片给药。常用的胆碱酯酶抑制剂包括多奈哌齐(Aricept, Adlarity)、加兰他明(Razadyne)和利瓦斯替明透皮贴剂(Exelon)。
The main side effects of these drugs include diarrhea (腹泻), nausea (恶心), loss of appetite and sleep disturbances (睡眠障碍). In people with certain heart disorders, serious side effects may include an irregular heartbeat (心律不齐).
这些药物的主要副作用包括腹泻、恶心、食欲不振和睡眠障碍。对于患有某些心脏疾病的人,严重的副作用可能包括心律不齐。
Memantine 美金刚 (,商品名Namenda). This medicine works in another brain cell communication network and slows the progression of symptoms with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s disease. It’s sometimes used in combination with a cholinesterase inhibitor. Relatively rare side effects include dizziness (头晕)and confusion (神志不清).
美金刚胺(加入盐酸):这种药物在另一种脑细胞通讯网络中起作用,减缓中度至重度阿尔茨海默病症状的进展。它有时与胆碱酯酶抑制剂联合使用。相对罕见的副作用包括头晕和神志不清。
Some medicines, such as sleep aids, anti-anxiety drugs, anticonvulsants (抗惊厥药), and antipsychotics (抗精神病药) warrant extra caution for people living with Alzheimer’s. These drugs should only be used with caution. (from .mayoclinic.org)
一些药物,如助眠药、抗焦虑药、抗惊厥药和抗精神病药,需要对阿尔茨海默病患者格外小心。这些药物只能谨慎使用。
Non-drug interventions for Alzheimer’s disease 非药物治疗
Non-drug interventions for Alzheimer’s disease include things like memory training, mental and social stimulation, and physical exercise programs. Some of these strategies could possibly improve people’s cognitive performance and increase their independence.
阿尔茨海默病的非药物干预包括记忆训练、精神和社会刺激以及体育锻炼项目。其中一些策略可能会改善人们的认知表现,增强他们的独立性。
