What’s the function of lungs? 肺的功能是什么?
The main function of the lungs (肺) is the process of gas exchange called respiration or breathing (呼吸). In respiration, oxygen from incoming air enters the blood, and carbon dioxide (二氧化碳), a waste gas from the metabolism (新城代谢), leaves the blood. A reduced lung function means that the ability of lungs to exchange gases is reduced. (eea.europa.eu)
肺的主要功能是气体交换过程,称为呼吸(或呼吸)。在呼吸过程中,空气中的氧气进入血液,新陈代谢产生的废气二氧化碳离开血液。肺功能降低意味着肺交换气体的能力降低。
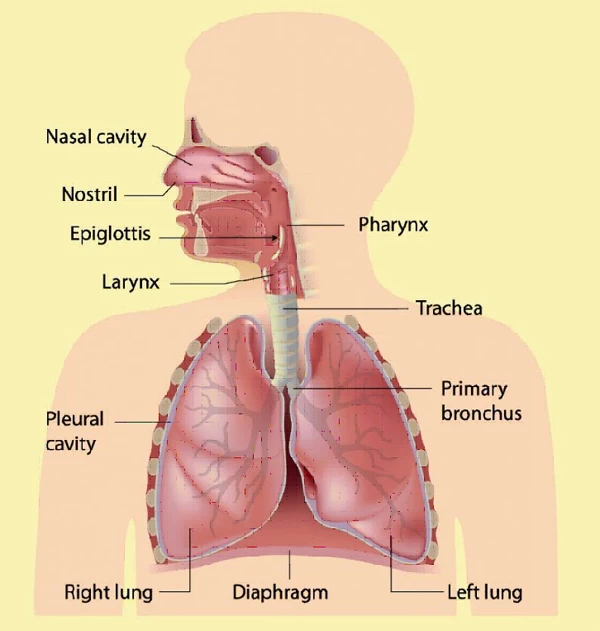
英语呼吸系统主要词汇:
Nasal cavity 鼻腔
Nostril 鼻孔
Pharynx 咽 /ˈfær.ɪŋks/
Larynx 候 /ˈlær.ɪŋks/
Epiglottis 会厌 /ˌep.əˈɡlɑː.t̬ɪs/
Trachea 气管 /ˈtreɪ.kiə/
Primary bronchus 支气管 /ˈbrɑːŋ.kəs/
Pleural cavity 胸膜腔 /ˈplʊr.əl/
Right lung 右肺
Left lung 左肺
Diaphragm 隔膜 /ˈdaɪ.ə.fræm/
What is pneumonia? 什么是肺炎?
Pneumonia ( 肺炎 /nuːˈmoʊ.njə/ )is inflammation (炎症) and fluid in your lungs caused by a bacterial, viral or fungal infection. It makes it difficult to breathe and can cause a fever and cough with yellow, green or bloody mucus (粘液/ˈmjuː.kəs/). The flu, COVID-19 and pneumococcal (肺炎球菌 / ˌnuː.moʊˈkɑː.kəl/)disease are common causes of pneumonia. Treatment depends on the cause and severity of pneumonia. (clevelandclinic.org)
肺炎是由细菌、病毒或真菌感染引起的肺部炎症和积液。它使呼吸困难,并可引起发烧和咳嗽,粘液呈黄色、绿色或带血。流感、COVID-19和肺炎球菌病是肺炎的常见病因。治疗取决于肺炎的病因和严重程度。
How can I tell if I have pneumonia versus the common cold or the flu?
如何分辨我是得了肺炎、普通感冒还是流感?
It can be difficult to tell the difference between the symptoms of a cold, the flu and pneumonia, and only a healthcare provider can diagnose you. As pneumonia can be life-threatening, it’s important to seek medical attention for serious symptoms that could be signs of pneumonia, such as:
很难区分感冒、流感和肺炎的症状,只有医疗保健提供者才能诊断出你的症状。由于肺炎可能危及生命,因此对可能是肺炎征兆的严重症状寻求医疗护理非常重要,例如:
Congestion (鼻腔堵塞)or chest pain.
Difficulty breathing.
A fever of 102 degrees Fahrenheit (38.88 degrees Celsius) or higher.
Coughing up yellow, green or bloody mucus or spit. (clevelandclinic.org)
鼻腔堵塞或胸痛。
呼吸困难。
发烧102华氏度(38.88摄氏度)或更高
咳出黄色、绿色或带血的粘液或唾液。
How is pneumonia diagnosed? 如何诊断肺炎?
To diagnose pneumonia, a healthcare provider will ask about your health history and conduct a physical exam. They’ll listen to your lungs with a stethoscope (听诊器/ˈsteθ.ə.skoʊp/)and may perform or order additional tests. These include imaging (成像) (like chest X-rays), pulse oximetry (血氧测定/ɑːkˈsɪm.ə.tri/)(checking oxygen levels in your blood), blood tests or sputum (spit) tests. Even if your healthcare provider confirms that you have pneumonia, sometimes, they can’t find the exact cause. (clevelandclinic.org)
为了诊断肺炎,医生会询问你的健康史并进行体检。他们会用听诊器听你的肺,可能会进行或安排额外的检查。这些检查包括成像(如胸部x光)、脉搏血氧仪(检查血液中的氧含量)、血液检查或痰测试。即使你的医疗保健提供者确认你患有肺炎,有时,他们也找不到确切的原因。
How is pneumonia treated? 如何治疗肺炎?
Treatment for pneumonia depends on the cause — bacterial, viral or fungal (真菌) — and how serious your case is. In many cases, the cause can’t be determined and treatment is focused on managing symptoms and making sure your condition doesn’t get worse. Some treatments may include:
肺炎的治疗取决于病因——细菌、病毒或真菌——以及病情的严重程度。在许多情况下,病因无法确定,治疗的重点是控制症状,确保你的病情不会恶化。一些治疗方法包括:
Antibiotics (抗生素): Antibiotics treat bacterial pneumonia (细菌性肺炎). They can’t treat a virus (病毒)but a provider may prescribe them if you have a bacterial infection at the same time as a virus.
抗生素:抗生素治疗细菌性肺炎。它们不能治疗病毒,但如果你同时感染了细菌和病毒,医生可能会给你开这种药。
Antifungal medications (抗真菌药物): Antifungals can treat pneumonia caused by a fungal infection (真菌感染引起的肺炎).
抗真菌药物:抗真菌药物可以治疗由真菌感染引起的肺炎。
Antiviral medications (抗病毒药物): Viral pneumonia (:病毒性肺炎)usually isn’t treated with medication and can go away on its own. A provider may prescribe antivirals such as oseltamivir (Tamiflu®), zanamivir (Relenza®) or peramivir (Rapivab®) to reduce how long you’re sick and how sick you get from a virus.
抗病毒药物:病毒性肺炎通常不需要药物治疗,可以自行消失。医生可能会给你开一些抗病毒药物,比如奥司他韦(达菲®)、扎那米韦(乐感清®)或帕拉米韦(Rapivab®),以缩短你的患病时间和感染病毒的程度。
Oxygen therapy (氧气疗法): If you’re not getting enough oxygen, a provider may give you extra oxygen through a tube in your nose or a mask on your face.
氧气疗法:如果你没有得到足够的氧气,医生可能会通过你鼻子里的管子或你脸上的面罩给你额外的氧气。
IV fluids (静脉输液): Fluids delivered directly to your vein (IV) treat or prevent dehydration (脱水).
静脉输液:直接输送到静脉(IV)的液体,用于治疗或防止脱水。
Draining of fluids (排空液体): If you have a lot of fluid between your lungs and chest wall (pleural effusion), a provider may drain it. This is done with a catheter (导管 /ˈkæθ.ə.t̬ɚ/)or surgery. (clevelandclinic.org)
排空液体:如果你的肺和胸壁之间有大量液体(胸腔积液),医生可能会将其排空。这是通过导管或手术完成的。
