What is periodontitis? 什么是牙周炎?
Periodontitis (牙周炎/ˌper.i.oʊ.dɑːn.ˈtaɪ.t̬ɪs/), also called gum disease (牙龈疾病), is a serious gum infection that damages the soft tissue around teeth. Without treatment, periodontitis can destroy the bone that supports your teeth. This can cause teeth to loosen or lead to tooth loss.
牙周炎,也被称为牙龈疾病,是一种严重的牙龈感染,会损害牙齿周围的软组织。如果不进行治疗,牙周炎会破坏支撑牙齿的骨骼。这可能会导致牙齿松动或导致牙齿脱落。
Periodontitis is common but can usually be prevented. It’s often the result of not taking care of your mouth and teeth. To help prevent periodontitis or improve your chance of successful treatment, brush at least twice a day, floss daily and get regular dental checkups. ( from mayoclinic.org)
牙周炎很常见,但通常是可以预防的。这通常是不注意口腔和牙齿的结果。为了帮助预防牙周炎或提高成功治疗的机会,每天至少刷牙两次,每天使用牙线,并定期进行牙齿检查。
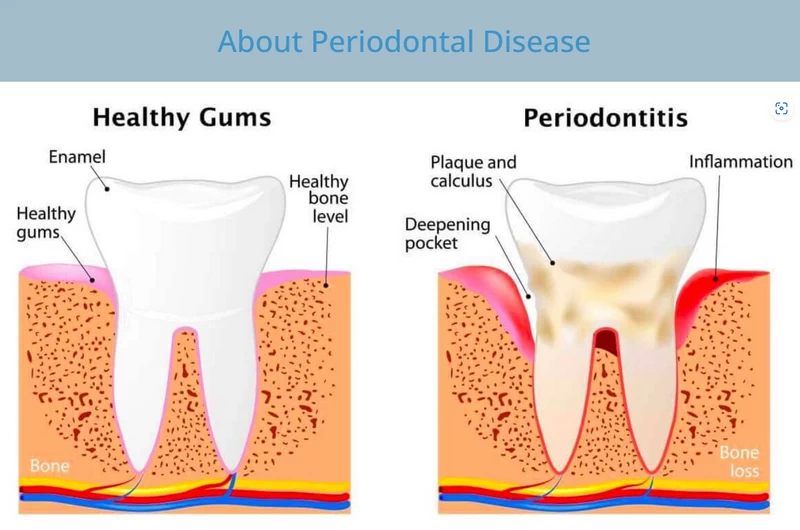
What causes periodontitis? 牙周炎的病因是什么?
Bacteria in the mouth infect tissue surrounding the tooth causes inflammation around the tooth leading to periodontal disease. When bacteria stay on the teeth long enough, they form a film called plaque 牙斑 (, which eventually hardens to tartar (牙垢), also called calculus (牙石). Tartar build-up can spread below the gum line, which makes the teeth harder to clean. Then, only a dental health professional can remove the tartar and stop the periodontal disease process. (from cdc.gov)
口腔内的细菌感染牙齿周围的组织,引起牙齿周围的炎症,从而导致牙周病。当细菌在牙齿上停留足够长的时间时,它们会形成一层叫做牙菌斑的膜,最终硬化成牙垢,也叫牙石。牙垢会扩散到牙龈线以下,使牙齿更难清洁。然后,只有牙科保健专业人员才能去除牙垢,阻止牙周病的发展。
What are the symptoms of periodontal disease?
The following are warning signs of periodontal disease:
以下是牙周病的警告信号:
Bad breath or bad taste that won’t go away
难闻的口气和难闻的味道不会消失
Red or swollen gums
牙龈红肿
Tender or bleeding gums
牙龈疼痛或出血
Painful chewing
痛苦的咀嚼
Loose teeth
牙齿松动
Sensitive teeth
敏感的牙齿
Gums that have pulled away from your teeth
牙龈从牙齿上脱落
Any change in the way your teeth fit together when you bite
当你咬合的时候,你的牙齿是否发生了变化
Any change in the fit of partial dentures ( from cdc.gov)
How to treat periodontitis? 如何治疗牙周炎?
Treatment may be done by a dentist or a periodontist (牙周病专家). A periodontist is a dentist who specializes in gum disease. A dental hygienist may work with your dentist or periodontist as part of your treatment plan. The goal of treatment is to thoroughly clean the pockets (牙袋) around teeth and prevent damage to surrounding gum tissue and bone. You have the best chance for successful treatment when you also have a daily routine of good oral care, manage health conditions that may impact dental health and stop tobacco use.
治疗可以由牙医或牙周病专家进行。牙周病专家是专门研究牙龈疾病的牙医。作为治疗计划的一部分,牙科保健师可能会与牙医或牙周病专家一起工作。治疗的目的是彻底清洁牙齿周围的牙袋,防止周围的牙龈组织和骨骼受损。当你有良好的日常口腔护理,管理可能影响牙齿健康的健康状况并停止使用烟草时,你获得成功治疗的机会最大。
Nonsurgical treatments 非手术治疗
If periodontitis isn’t advanced, treatment may involve less invasive procedures, including:
如果牙周炎不严重,治疗可以采用侵入性较小的方法,包括:
Scaling (洁治术): Scaling removes tartar and bacteria from your tooth surfaces and below your gumline. It may be done using instruments, a laser or an ultrasonic device (激光或超声波设备).
洁治术。洗牙可以清除牙齿表面和牙龈线以下的牙垢和细菌。它可以使用仪器,激光或超声波设备来完成。
Root planing (根面平整术):Root planing smooths the root surfaces. This helps prevent further buildup of tartar and bacteria. It also helps your gums attach to your teeth again.
根面平整术:根面平整术使根表面光滑。这有助于防止牙垢和细菌的进一步积聚。它还可以帮助你的牙龈再次附着在牙齿上。
Antibiotics (抗生素). Topical (局部的)or oral antibiotics can help control bacterial infection. Topical antibiotics can include antibiotic mouth rinses or putting gel containing an antibiotic into gum pockets. Sometimes oral antibiotics are needed to get of bacteria that cause infections.
抗生素。局部或口服抗生素可以帮助控制细菌感染。局部抗生素可以包括抗生素漱口水或将含有抗生素的凝胶放入牙龈袋。有时需要口服抗生素来清除引起感染的细菌。
Surgical treatments 手术治疗
If you have advanced periodontitis, you may need dental surgery, such as:
如果你有严重的牙周炎,你可能需要牙科手术,例如:
Flap surgery (皮瓣手术,俗称的牙龈手术), also called pocket reduction surgery. Your periodontist makes cuts in your gums to carefully fold back the tissue. This exposes the tooth roots for more effective scaling and root planing. Because periodontitis often causes bone loss, the underlying bone may be reshaped before the gum tissue is stitched back in place. After you heal, it’s easier to clean the areas around your teeth and maintain healthy gum tissue.
皮瓣手术,也叫口袋缩小手术。牙周病医生会在你的牙龈上切开,小心地将组织折叠起来。这样可以使牙根暴露出来,以便更有效地清洁牙根。由于牙周炎经常导致骨质流失,在将牙龈组织缝合回原位之前,可能会对下面的骨骼进行重塑。愈合后,更容易清洁牙齿周围的区域,保持健康的牙龈组织。
Soft tissue grafts (软组织移植). When you lose gum tissue, your gumline gets lower, exposing some of your tooth roots. You may need to have some of the damaged tissue reinforced. This is usually done by removing a small amount of tissue from the roof of your mouth or using tissue from another donor source and attaching it to the affected site. This can help reduce further gum loss, cover exposed roots and give your teeth a better appearance.
软组织移植。当你失去牙龈组织时,你的牙龈线会变低,露出一些牙根。你可能需要对一些受损组织进行加固。这通常是通过从你的上颚移走少量组织或使用其他供体来源的组织并将其附着在受影响的部位来完成的。这可以帮助减少牙龈的进一步流失,覆盖暴露的牙根,让你的牙齿看起来更好。
Bone grafting (骨移植)。 This procedure is performed when periodontitis destroys the bone around your tooth root. The graft may be made from small bits of your own bone, or the bone may be made of artificial material or donated. The bone graft helps prevent tooth loss by holding your tooth in place. It also serves as a platform for the regrowth of natural bone.
骨移植。当牙周炎破坏了牙根周围的骨头时,就需要进行这个手术。移植物可以由你自己的小块骨头制成,也可以由人工材料制成或捐赠。植骨可以通过固定牙齿来防止牙齿脱落。它还可以作为自然骨骼再生的平台。
Guided tissue regeneration (引导组织再生)。This allows the regrowth of bone that was destroyed by bacteria. In one approach, your dentist places a special type of fabric between existing bone and your tooth. The material prevents unwanted tissue from growing into the healing area, allowing bone to grow back instead.
引导组织再生。这使得被细菌破坏的骨头能够再生。在一种方法中,你的牙医在现有的骨头和牙齿之间放置一种特殊的织物。这种材料可以防止不需要的组织生长到愈合区域,从而使骨骼重新生长。
Tissue-stimulating proteins(组织刺激蛋白)。 Another approach involves applying a special gel to a diseased tooth root. This gel contains the same proteins found in developing tooth enamel and stimulates the growth of healthy bone and tissue. ( from mayoclinic.org)
组织刺激蛋白。另一种方法是将一种特殊的凝胶涂在患病的牙根上。这种凝胶含有与发育中的牙釉质相同的蛋白质,可以刺激健康骨骼和组织的生长。


