When you think of Beijing, towering skyscrapers, the Great Wall, and the Forbidden City may come to mind. But there’s a hidden gem tucked away in the heart of the city that often goes unnoticed—the Beijing Ancient Observatory.
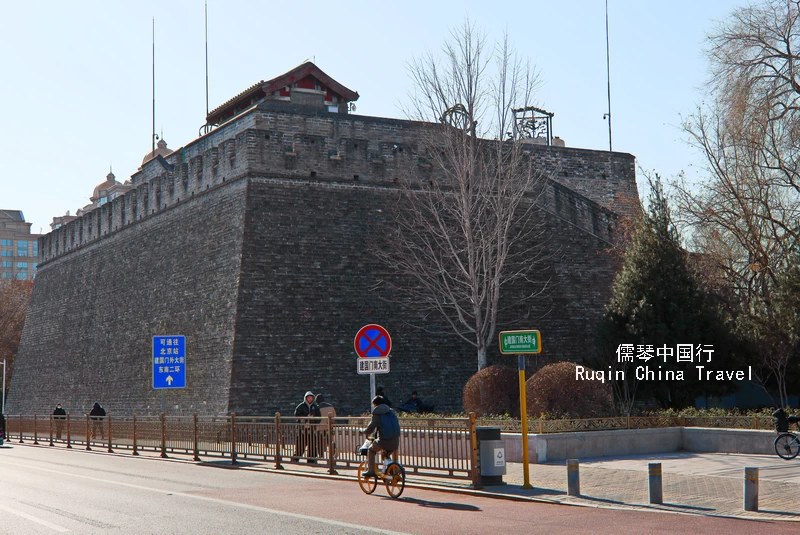

This quiet spot is a treasure trove for history lovers and those intrigued by ancient astronomy. It offers a fascinating look at China’s early scientific advancements, with its collection of ancient instruments and rich historical context.
In this guide, we’ll share everything you need to know about visiting this remarkable site—from how to get there to the best times to go, entrance fees, and what you can expect when you arrive. Ready for an off-the-beaten-path experience? Let’s dive in.
1. Beijing Ancient Observatory Overview
The Beijing Ancient Observatory was first built in the seventh year of the Ming Zhengtong reign (1442). It served as the royal astronomical observatory during the Ming and Qing dynasties and is one of the oldest existing observatories in the world.
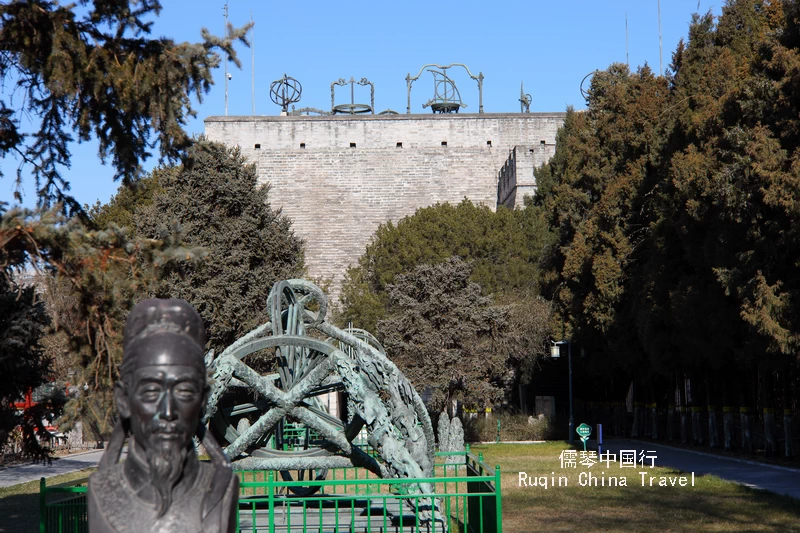

Rising 14 meters high, the observatory looks like a castle. On its rooftop, you’ll find eight remarkable astronomical instruments—blending both Chinese and Western science. These include armillary spheres, celestial globes, and azimuth theodolites, all reflecting China’s advanced understanding of the cosmos.
The Beijing Ancient Observatory has been observing the skies for nearly 500 years. Over this long period, it gathered vast amounts of astronomical data, making huge contributions to the field. Today, it still holds meteorological records from the Qing Dynasty, covering 180 years—one of the oldest and most complete weather records in the world.
Beyond astronomy, the observatory played a key role in the exchange between Chinese and Western cultures. During the Qing Dynasty, European methods were used to calculate the calendar, and new instruments were added to enhance the observatory’s capabilities. It’s a fascinating glimpse into how two worlds once came together to share knowledge.
During the Boxer Rebellion in 1900, five of these instruments were taken to Germany. However, under the Treaty of Versailles, they were returned to China in 1921. Today, the observatory stands proudly as a symbol of China’s rich scientific heritage, offering visitors a unique peek into the past.
In 1956, the observatory officially opened to the public as the “Beijing Ancient Astronomical Instruments Exhibition Hall.”
2. How to Get to Beijing Ancient Observatory
Getting to the Beijing Ancient Observatory is straightforward, thanks to its central location and the city’s efficient public transportation system. Whether you prefer taking the subway or a bus, the observatory is easily accessible.
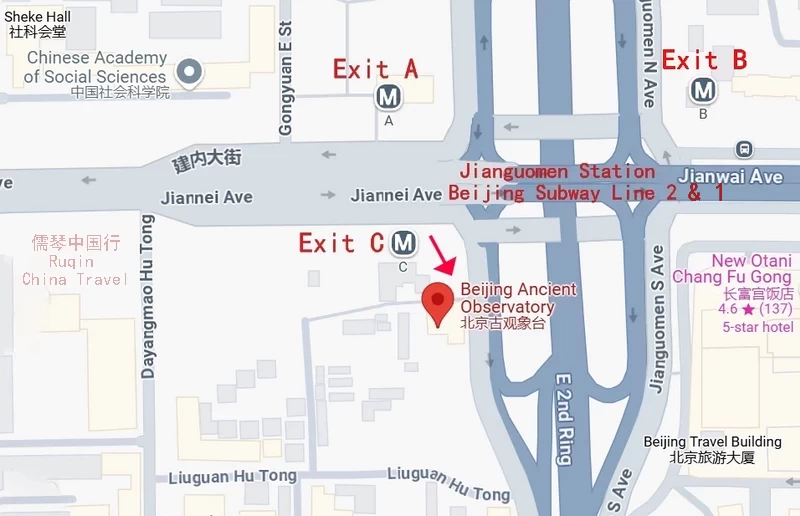
By Subway
The most convenient way to reach the Beijing Ancient Observatory is by subway. You can take either Subway Line 1 or Subway Line 2 and get off at Jianguomen Station (建国门站).
Once you arrive at the station, follow the signs to Exit C. After exiting, you’ll need to walk approximately 220 meters (250 yards) to reach the ticket office of the observatory. The walk is short and pleasant, offering you a quick view of the surrounding area as you approach the historical site.
By Bus
If you prefer to take a bus, there are several options available. You can take bus numbers 20, 39, 43, 44, 122, 139, 142, 637, or 638 and get off at the Jianguomen Nan (South Jianguomen) stop.
Once you disembark, walk northward along Jianguomen South Street for about 500 meters (547 yards) until you reach the ticket office of the Beijing Ancient Observatory. The walk from the bus stop to the observatory is straightforward, and you’ll be able to spot the observatory tower as you approach.
On Foot
You can easily walk to the Beijing Ancient Observatory. That’s exactly what I did on my last visit. I began by exploring the Beijing Ming City Wall Ruins Park. From there, I strolled north along the ancient city wall.
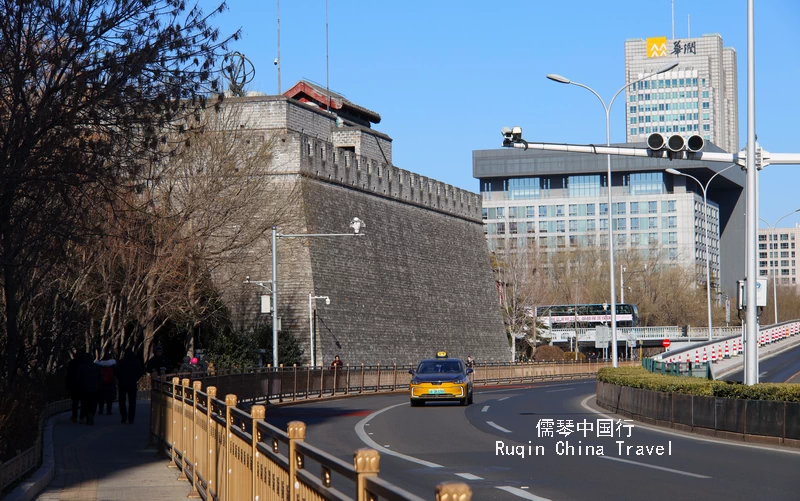

Before long, the observatory appeared in front of me, rising 3 meters above the wall and seamlessly blending into the surroundings. It was the perfect way to connect history with the present in a single walk.
3. Opening Hours and Entrance Fees
When planning your visit, it’s essential to know the opening hours and entrance fees to ensure you have enough time to explore this fascinating site.
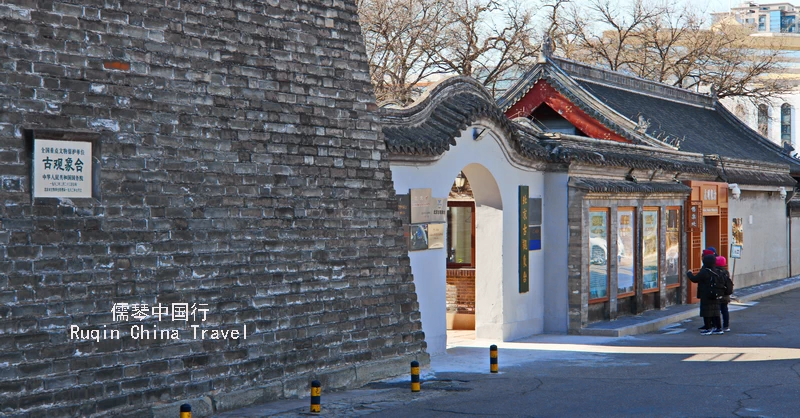

Opening Hours
The Beijing Ancient Observatory is open to the public from 9:00 AM to 5:00 PM daily. However, it is closed on Mondays and Tuesdays, so plan your visit accordingly. Note that ticket sales stop at 4:30 PM, so it’s best to arrive well before then to secure your entry.
Entrance Fees
The entrance fee to the Beijing Ancient Observatory is CNY 20. This fee grants you access to the entire site, including the tower and the eight ancient astronomical instruments on display and its bungalow exhibition halls.
Given the historical significance and the unique nature of the observatory, the entrance fee is quite reasonable and offers excellent value for the experience. People over 60 are free of charge.
4. Exploring the Beijing Ancient Observatory
Once you’ve arrived at the Beijing Ancient Observatory and purchased your ticket, it’s time to explore the site. Here’s what you can expect during your visit.
Siheyuan Exhibition Area (3 Halls)
As you step into the Beijing Ancient Observatory, look to your right. You’ll see a traditional Siheyuan courtyard entrance. Inside, you’re greeted by a spacious courtyard, which serves as a large exhibition area. The courtyard is divided into three wings: east, north, and west. Each wing holds a separate exhibition hall. Outdoors, you’ll find statues of famous astronomers from both China and beyond.

The exhibitions here are diverse and fascinating. The “Ancient Chinese Astronomy” exhibition explores China’s astronomical achievements and its exchanges with the West. In the “Chinese Starry Sky” exhibition, housed in the Ziwei Hall (紫微殿), you’ll see incredible instruments like the Guiding Car and Water Transport Instrument, showcasing China’s advanced astronomy.

The “Western Knowledge Entering China” exhibition in the West Wing focuses on the introduction of Western astronomy to China and its blending with local traditions.

Finally, the “Ling Tai Instruments” exhibition in the East Wing delves into the observatory’s history and the relationship between its instruments and China’s national fate. It’s an intriguing journey through the history of both Chinese and global astronomy.
The Tower and the 8 Instruments
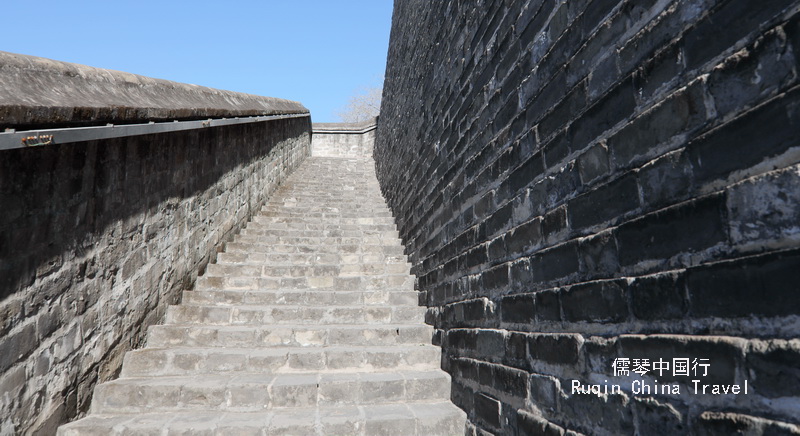
One of the standout features of the Beijing Ancient Observatory is its 14-meter-high, castle-like tower. To reach the top, you’ll climb 90 stone steps. While it’s not a difficult climb, it gives you a sense of the observatory’s grand scale.

At the top, the platform showcases eight remarkable bronze astronomical instruments. These were crafted during China’s golden ages—the Kangxi and Qianlong reigns.
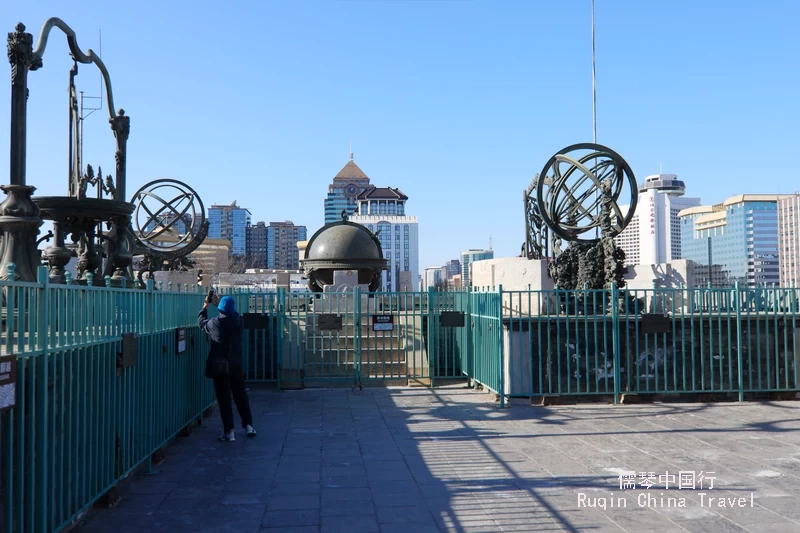

In 1900, these instruments were taken by France and Germany. France took three, including the Equatorial Coordinate Instrument, the Quadrant, and the Ecliptic Coordinate Instrument. Germany took five, including the Celestial Sphere, Meridian Instrument, and others. These were eventually returned to China and are now back at the observatory.
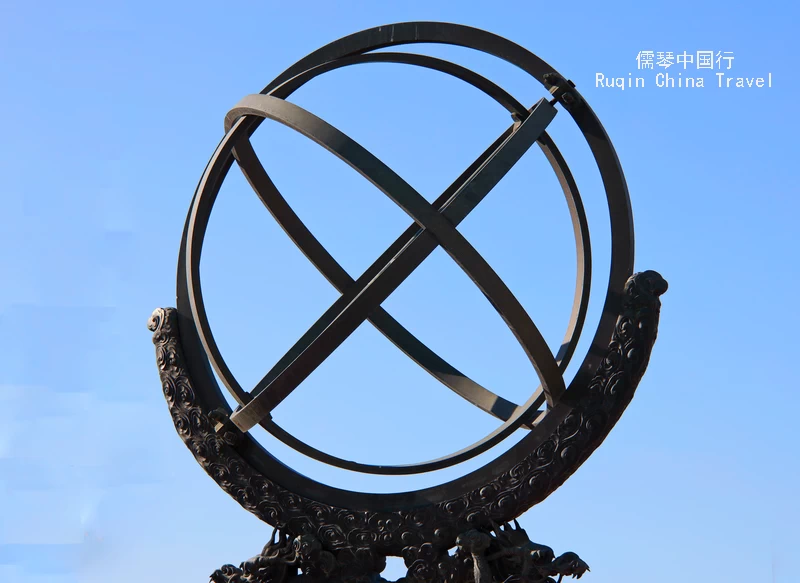

Ecliptic Armilla (黄道经纬仪) : This was China’s first instrument to observe using modern ecliptic coordinates. It was designed to track the movement of the sun and planets. Built between 1669 and 1673 under the supervision of the Belgian missionary Ferdinand Verbiest, it measures celestial longitude and latitude and determines the twenty-four solar terms.
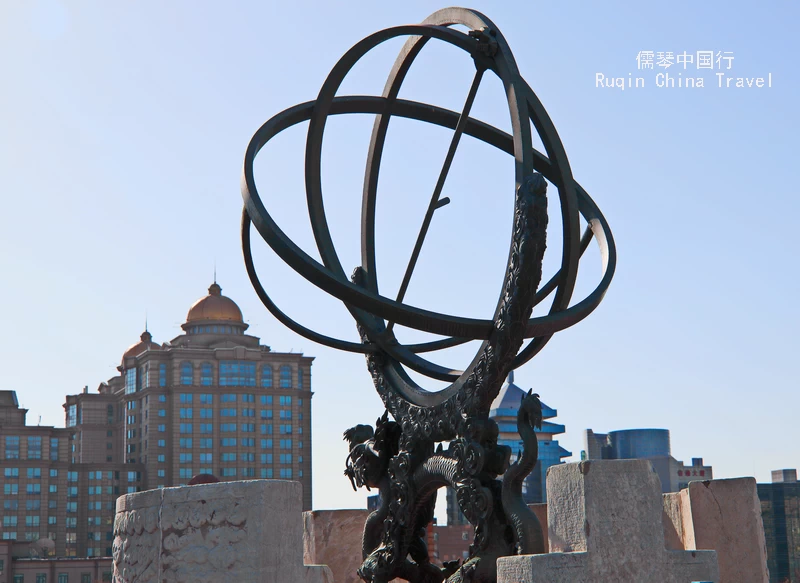

Equatorial Armilla (赤道经纬仪): Manufactured between 1669 and 1673, this instrument was used to measure the right ascension and declination of celestial bodies, along with solar time. It was also supervised by Ferdinand Verbiest.

Sextent (纪限仪): Used to measure the angular distance between celestial bodies within 60 degrees, as well as the angular diameter of the sun and moon. Like the other instruments, it was crafted between 1669 and 1673 by Verbiest.

Celestial Globe (天体仪): This instrument was used to calculate and demonstrate the positions of the sun, moon, and stars in the sky using three coordinate systems: ecliptic, equatorial, and horizon. Built between 1669 and 1673, it was also supervised by Verbiest.
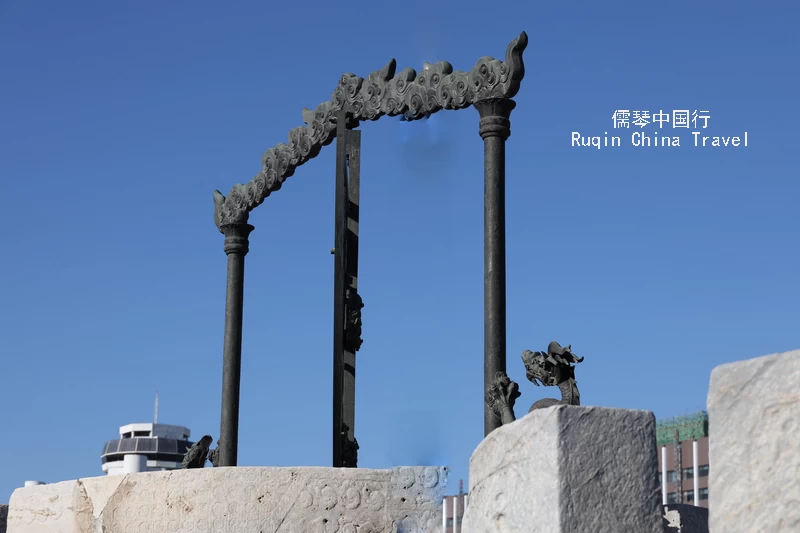

The Quadrant (象限仪): Used to measure the altitude or zenith distance of celestial bodies. Created between 1669 and 1673, it was another of Verbiest’s works.

Azimuth Theodolite(地平经纬仪): Designed to measure the meridian height of the sun and planets, helping to determine the location’s latitude, the ecliptic tilt, and the coordinates of stars in the observation site. This was cast in 1715 during the reign of Kangxi.
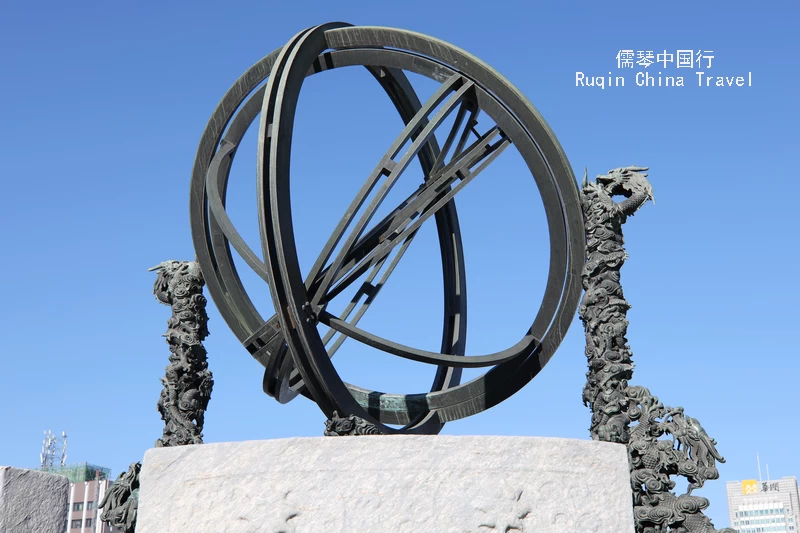

New Armilla (玑衡抚辰仪): Similar in function to the Equatorial Armilla , this device included a rotating equatorial ring to directly read the celestial longitude of a star. It was the final instrument to be completed in 1754, during the reign of Qianlong.

From the observatory’s tower, you’ll also be treated to spectacular views of Beijing. You can see the modern cityscape, including the towering China Zun building and the bustling Chang’an Street, stretching out before you. It’s an incredible mix of old and new, and a perfect spot to reflect on Beijing’s rich history.
Tips for Visiting the Beijing Ancient Observatory
To make the most of your visit to the Beijing Ancient Observatory, consider the following tips:
Best Time to Visit
The best time to visit the Beijing Ancient Observatory is during the morning or early afternoon. This timing allows you to avoid the late afternoon rush and ensures you have plenty of time to explore the site before it closes.
Additionally, visiting earlier in the day means you’ll have better lighting for viewing the instruments and taking photos.
What to Bring
When visiting the observatory, it’s a good idea to bring a camera, as the site offers numerous photo opportunities. The contrast between the ancient instruments and the modern city skyline creates a striking visual.
Also, consider bringing a bottle of water, especially during the warmer months, as the climb up the tower can be a bit strenuous.
Respecting the Site
As with all historical sites, it’s essential to be respectful during your visit. The Beijing Ancient Observatory is a significant cultural heritage site, and visitors should take care not to touch the instruments or climb on any structures outside of designated areas. By following these guidelines, you help preserve the site for future generations.
Nearby Attractions and City WalK
While the Beijing Ancient Observatory is a destination in itself, there are several other attractions nearby that you might want to explore during your visit for a city walk.
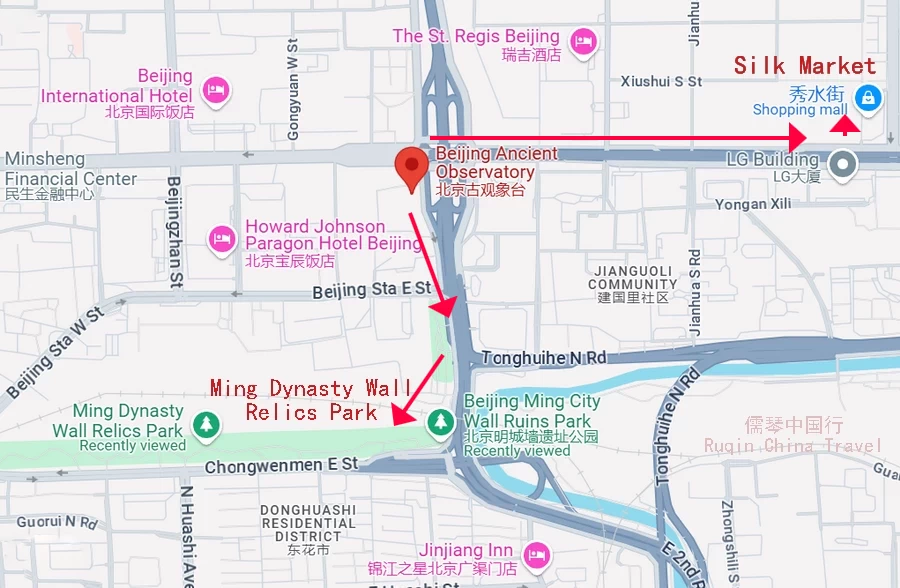
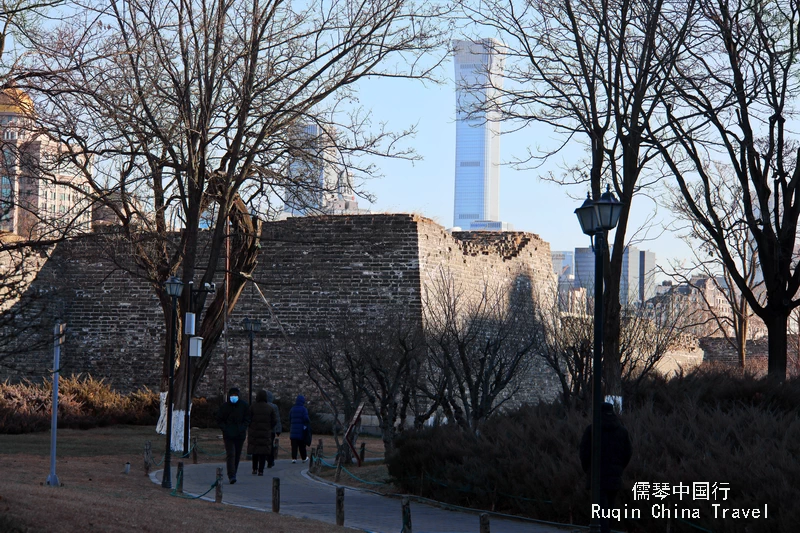
Ming Dynasty Wall Relics Park
A hidden gem in Beijing, the Ming Dynasty Wall Relics Park, also known as the Beijing Ming City Wall Ruins Park, offers a fascinating glimpse into China’s rich history. Located in the heart of Beijing, this park is not just a place for leisurely strolls; it’s a journey back in time.

Ritan Park
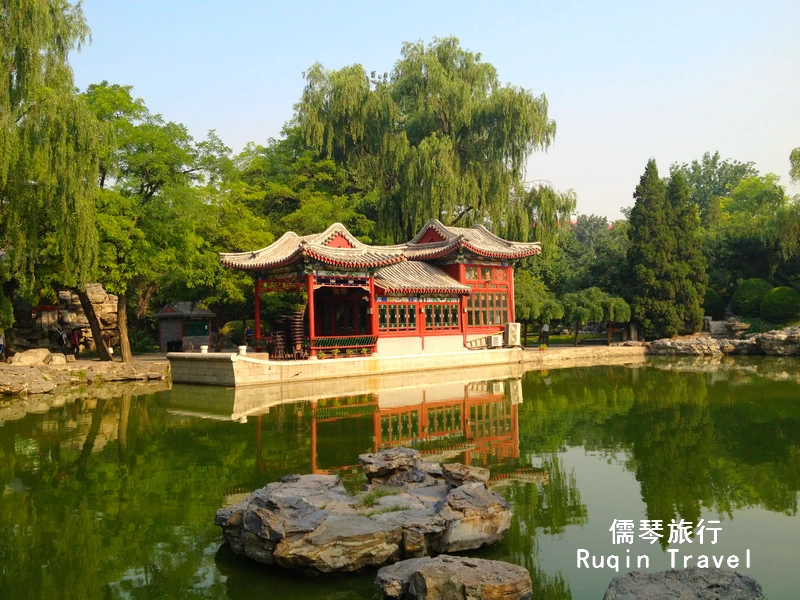
Just a short walk from the observatory, Ritan Park offers a peaceful retreat in the middle of the city. The park is home to the Temple of the Sun, one of Beijing’s five ancient altars. It’s a great place to relax and enjoy the natural beauty of the city after your visit to the observatory.

Silk Market Shopping Mall
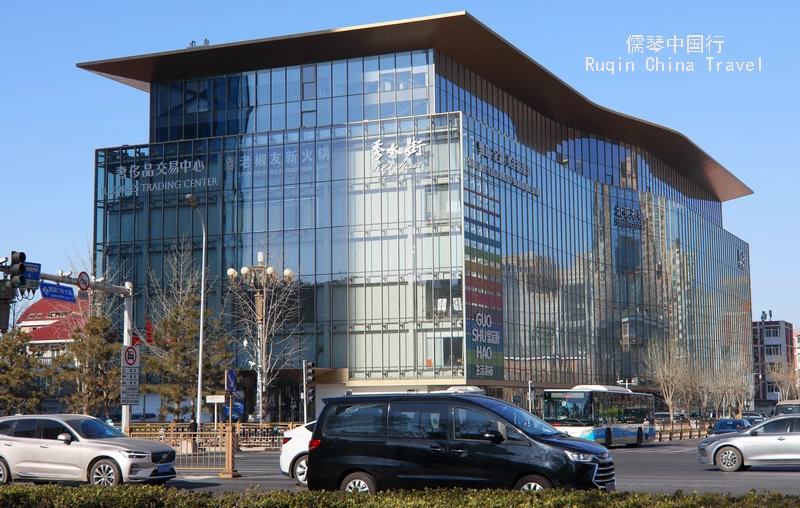
For those interested in shopping, the Silk Market is located near Jianguomen Station. This bustling market is famous for its wide variety of silk products, clothing, and souvenirs. It’s an excellent spot to pick up gifts or simply experience the vibrant atmosphere of a traditional Chinese market.

Whether you’re a history buff, an astronomy enthusiast, or simply a curious traveler, the Beijing Ancient Observatory is a site that should not be missed. By following this Beijing Ancient Observatory Travel Guide, you’ll be well-prepared to make the most of your visit and gain a deeper understanding of China’s remarkable scientific achievements.


